ANTISHICNC CNC Turning Milling Machines,CNC Lathes
ANTISHICNC CNC Turning Milling Machines,CNC Lathes
In the process of CNC lathe, tail-stock plays a vital role. Tailstock on CNC lathe is mainly divided into manual tail-stock, hydraulic tail-stock and pneumatic tail-stock of three types, the next by the ANTISHICNC engineers for you to introduce the three tail-stock in the mode of operation, tightening force control, response speed and precision and stability, there are significant differences.
1.Operation mode
Manual tail-stock:
Mainly rely on manual operation. By turning the hand-wheel or handle to achieve the tail-stock movement and tightening action.
For example, the operator needs to slowly turn the hand-wheel by hand, so that the tail-stock along the guide rail to move to the appropriate position, and then by rotating the other handle to control the tail-stock top top tighten the work-piece. This process is relatively tedious and requires a certain amount of physical strength and operating experience.
The accuracy of the operation depends on the skill level of the operator, and inexperienced operators may experience inaccurate position adjustment or uneven tightening force.
 |
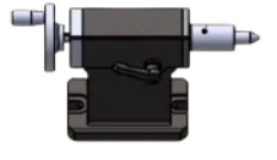 |
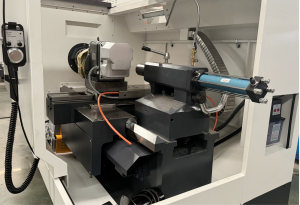
Hydraulic tail-stock:
Driven using a hydraulic system. The movement of the tail-stock is controlled by operating buttons or commands from the CNC.
When a command is received, a cylinder in the hydraulic system pushes the tail-stock to move and tighten the work-piece. The hydraulic system provides a high clamping force and is suitable for machining heavier or larger work-pieces.
The operation is relatively simple, and can achieve more accurate position control and adjustment of the jacking force. For example, different parameters can be set in the CNC system to meet the machining requirements of different work-pieces.
 |
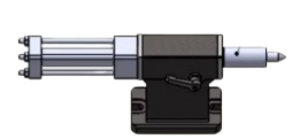 |
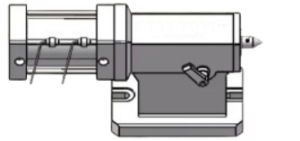
Pneumatic tail-stock:
Uses compressed air as a power source. The movement and jacking of the tail-stock is controlled by a pneumatic control valve.
The pneumatic system has a fast response time and quick action. However, due to the compressibility of air, the tightening force of the pneumatic tail-stock is relatively small, suitable for some light or small work-piece processing.
Convenient operation, only through the control of the valve switch to achieve the tail-stock action. However, a stable air supply is required, and attention should be paid to the adjustment of air pressure to ensure the tail-stock’s normal operation.
2.Tightening force control
Manual tail-stock:
Tightening force mainly depends on the operator’s feeling and experience to control. It is difficult to achieve precise adjustment of the top tightening force, and it is easy to have the situation that the top tightening force is too big or too small.
If the tightening force is too small, the work-piece may loosen during machining, affecting the machining accuracy; if the tightening force is too large, it may damage the work-piece or the centre.
For example, when machining work-pieces of different materials and sizes, the operator needs to keep trying and adjusting to find the right jacking force.
Hydraulic tail-stock:
The amount of jacking force can be precisely controlled by a pressure regulating valve in the hydraulic system. It can be adjusted according to the requirements of different work-pieces to ensure the stability and consistency of the tightening force.
The hydraulic system can provide large jacking force, which is suitable for processing heavy work-pieces. At the same time, due to the stability of the hydraulic system, the jacking force is not easy to change during the machining process, which is conducive to improving machining accuracy.
For example, in CNC machining, different parameters of the top tightening force can be set by programming to meet the machining requirements of different processes.
Pneumatic tail-stock:
The ejector force is relatively small and difficult to control accurately. Due to the compressibility of air, the tightening force of pneumatic tail-stock will be affected by factors such as air pressure fluctuation and cylinder leakage.
Generally, it is suitable for light work-piece machining which does not require high tightening force. In the process of using, it is necessary to pay attention to the stability of air pressure and the sealing of the cylinder to ensure the reliability of the tightening force.
For example, for the processing of some small parts, pneumatic tail-stock can quickly achieve the top tightening and loosening action, but the accuracy of the top tightening force may not be as good as hydraulic tail-stock.
3.The response speed
Manual tail-stock:
The response speed is the slowest. The operator needs to manually turn the hand-wheel or handle to move the tail-stock, this process is relatively slow, especially in the case of needing to frequently adjust the tail-stock position, it will affect the processing efficiency.
For example, when a work-piece needs to be changed or machining parameters need to be adjusted, it may take longer to manually operate the tail-stock.
Hydraulic tail-stock:
Faster response. The hydraulic system transmits power quickly, allowing the tail-stock to quickly move and tighten the work-piece when commanded to do so.
It is suitable for CNC machining with a high degree of automation and can increase productivity. For example, during continuous machining, the hydraulic tail-stock can respond quickly to CNC system commands to achieve efficient machining operations.
Pneumatic tail-stock:
The response speed is very fast. Compressed air can quickly push the cylinder action, so that the tail-stock can move and tighten in an instant.
For some need to quickly change the work-piece or make frequent adjustments to the processing occasions, pneumatic tail-stock has great advantages. For example, in the batch processing of some small parts, the pneumatic tail-stock can achieve rapid tightening and loosening, and improve production efficiency.
4.Precision and stability
| Manual tail-stock |
| Precision and stability are relatively low.
Manual operation is easily affected by human factors, such as uneven operating force, inaccurate position adjustment. After long-term use, the guide rail and screw of the manual tail-stock may wear out, resulting in unstable tail-stock movement and affecting machining accuracy. For example, when carrying out high-precision machining, the manual tail-stock may not be able to meet the requirements, and it is necessary to use other auxiliary tools to improve the accuracy. |
| Hydraulic tail-stock |
| Higher precision and stability.
The hydraulic system can provide smooth power output, so that the tail-stock movement and tightening more accurate and stable. The sealing of the hydraulic system is good, which can reduce the interference of external factors and ensure the machining accuracy. At the same time, the pressure of the hydraulic system can be kept relatively stable, which is conducive to improving the consistency of machining. For example, in precision machining, the hydraulic tailstock can ensure the machining accuracy of the workpiece through precise position control and stable ejector force. |
| Pneumatic tailstock |
| Accuracy and stability are average.
Due to the compressibility of air, the position control and tightening force of pneumatic tail-stock may be affected to some extent. However, for some machining occasions that do not require high precision, the quick response and easy operation of pneumatic tail-stock can make up for its lack of precision. For example, in some simple machining tasks, the pneumatic tailstock can meet the basic machining requirements, and can improve productivity. |
In summary, the manual tail stock, hydraulic tail stock and pneumatic tail stock on CNC lathe have their own characteristics and applicable scenes. In the actual application, according to the processing needs, work-piece characteristics and production efficiency and other factors should be considered to choose the appropriate tail-stock type, in order to give full play to the advantages of CNC lathe processing, improve production quality and efficiency.